The management of industrial waste is regulated through the Environment Protection Act 2017(opens in a new window) and Environment Protection Regulations 2021(opens in a new window).
Determining whether your material is considered waste or not helps you to understand what duties and responsibilities apply to you. Learn more about what is waste.
Managing industrial waste involves:
- Classifying – industrial waste must be classified so that its clear what duties apply and how to manage it.
- Transporting – both the transporter and the person permitting the transport have duties they must meet.
- Depositing and receiving – waste must be taken to a place that is authorised to receive it (lawful place).
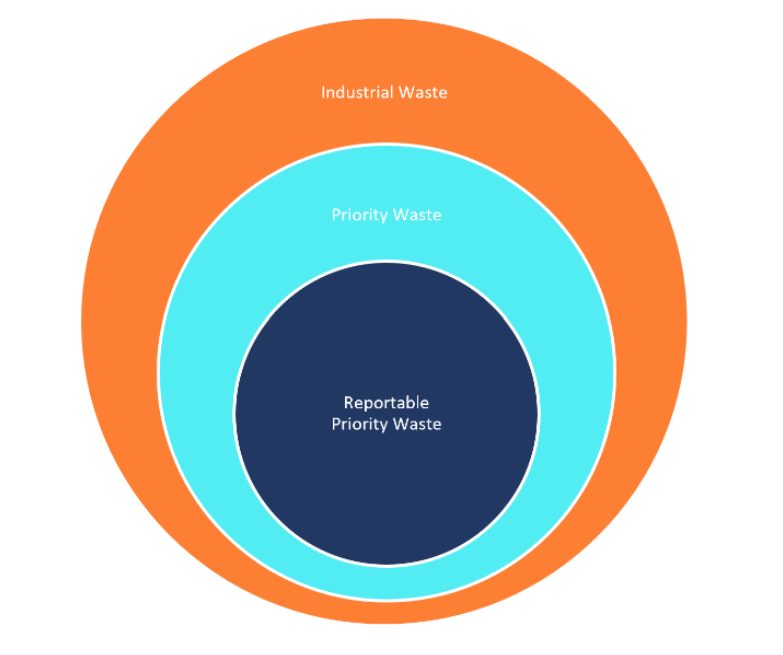
Industrial waste is classified according to the risk and the potential for mismanagement:
- industrial waste
- priority waste – waste with higher risks, requiring more regulation
- reportable priority waste – waste with highest risks, requiring greatest regulation.
Priority waste is a subset of industrial waste. Reportable priority waste is a subset of priority waste. The duties and obligations associated with these waste classifications accumulate.
Under the Act, there are 7 industrial waste duties. The duties set out the legal responsibilities for managing industrial waste. If you manage or control industrial waste, you must:
- classify your industrial waste
- meet the duties that apply to the waste classification.
You manage or control industrial waste if you:
- produce or generate it
- collect, consign, transfer or transport it
- receive, handle or store it
- undertake resource recovery or process it
- dispose of it.
The general environmental duty applies more broadly to anyone involved in any industrial waste management activity.
Managing industrial waste is complex. We appoint accredited consigners to support businesses to meet their waste duties. To learn more, visit Accredited consigners for managing industrial waste.
Industrial waste
Industrial waste is all waste from:
- commercial, industrial and trade activities
- laboratories
- households, once the waste arrives at a waste facility – for example, a transfer station or landfill
- accommodation, cafes and restaurants
- building and road construction, renovations, demolitions and repairs
- primary industries, like agriculture, forestry and fishing.
Industrial waste also includes any waste transported for fee or reward from any source other than the collection of kerbside waste by or on behalf of a council.
Kerbside waste collected by or on behalf of a council is not industrial waste at the time it's collected. It only becomes industrial waste once it reaches a waste or resource recovery facility.
Duties that apply to industrial waste
The duties that apply to industrial waste – including priority waste and reportable priority waste – are:
- duties of persons depositing industrial waste
- duty of persons involved in transporting industrial waste
- duties of persons receiving industrial waste
- general environmental duty.
Visit these pages to learn what you must do to comply with the law.
Priority waste
Priority waste is a subset of industrial waste. Examples include:
This type of waste has greater regulatory controls and duties because it:
- is prone to mismanagement
- is harmful to human health or the environment
- has potential for reuse or recycling.
For some priority waste, you must identify the relevant priority waste category. This applies to:
- priority waste going to landfill
- soil that is priority waste.
What the priority waste category is depends on how hazardous the waste is. The category tells you:
- which landfills can receive the waste
- the waste levy you need to pay to dispose of the waste at the landfill.
If you’re managing soil, the category indicates your options for:
- onsite and offsite management of the waste soil
- disposal of the waste soil.
Duties that apply to priority waste
All of the industrial waste duties plus additional duties apply to priority waste:
- duties of persons depositing industrial waste
- duty of persons involved in transporting industrial waste
- duties of persons receiving industrial waste
- duties of persons managing priority waste
- duty to investigate alternatives to waste disposal
- general environmental duty.
Visit these pages to learn what you must do to comply with the law.
For information on requirements for managing contaminated soil waste, visit Contaminated land and groundwater.
Reportable priority waste
Reportable priority waste is a subset of priority waste and carries the highest level of controls.
This type of waste usually poses the greatest risk to human health and the environment. It includes solvents, acids and contaminated soils.
As with priority waste, reportable priority waste has greater regulatory controls and duties. This is because it:
- is prone to mismanagement
- is harmful to human health or the environment.
Some reportable priority wastes are also classed as dangerous goods. Special storage and handling requirements apply to dangerous goods.
Duties that apply to reportable priority waste
All of the 7 waste duties and the general environmental duty apply to reportable priority waste:
- duties of persons depositing industrial waste
- duty of persons involved in transporting industrial waste
- duties of persons receiving industrial waste
- duties of persons managing priority waste
- duty to investigate alternatives to waste disposal
- duty to notify of transaction in reportable priority waste
- duty of persons transporting reportable priority waste
- general environmental duty.
Waste tyres are an exception to this. Waste tyres are classified as reportable priority waste, but the duty of persons transporting reportable priority waste does not apply to waste tyres. All other duties apply.
Visit these pages to learn what you must do to comply with the law.
Updated